What is Identity Access Management (IAM)?
What is Identity Access Management (IAM)?

As organizations rely more on digital systems, securing access to critical data and applications is essential. Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a framework of policies and technologies that helps businesses manage digital identities and control user access.
By verifying identities and enforcing security measures, IAM ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information, reducing cybersecurity risks.
For those asking, what is IAM in cybersecurity? It is a critical security measure that protects organizations from unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats.
A well-defined IAM policy sets rules for authentication, authorization, and access control, while a strong IAM framework helps businesses manage roles, permissions, and compliance requirements.
With the rise of cloud computing and remote work, IAM in cloud computing ensures secure access across multiple platforms. Many enterprises also use federated identity & access management, allowing users to log in once and access multiple systems seamlessly.
This guide explores the fundamentals of IAM, its role in securing organizational access, and how identity access management solutions help businesses protect data while providing seamless access for users.
1. Why Your Organization Needs IAM Solutions
As businesses expand and embrace digital transformation, securing access to systems and data becomes more critical than ever. Without robust identity access management solutions, organizations face growing security risks, compliance challenges, and operational inefficiencies. A well-implemented IAM strategy not only strengthens security but also enhances compliance and streamlines business operations.
Challenges Businesses Face Without Robust IAM
Without a structured workforce IAM system, organizations struggle with managing user access efficiently. Unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats become significant risks, especially in remote and hybrid work environments.
Manual provisioning and de-provisioning processes create security gaps and increase administrative overhead, making it harder to control who can access critical business resources.
How IAM Mitigates Security Risks and Supports Compliance
A strong IAM risk management framework helps organizations reduce security vulnerabilities by enforcing strict authentication measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC). IAM also plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance, ensuring businesses meet data protection standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. By providing access logs, audit trails, and automated compliance reporting, IAM simplifies regulatory adherence and minimizes the risk of penalties.
Elevating Security, Operational Agility, and Cost Efficiency with IAM
Implementing a robust identity access management solution provides several key benefits that enhance security, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
1. Streamlined Operations
- Automated Access Management – IAM automates user access reviews, access approvals, and de-provisioning, reducing administrative burden.
- Improved IT Efficiency – Minimizes manual access management efforts, allowing IT teams to focus on critical tasks.
- Simplified Compliance Management – Ensures compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS by enforcing access controls and maintaining detailed audit logs.
2. Enhanced User Experience
- Seamless Authentication – Features like single sign-on (SSO) allow users to access multiple applications with a single login, eliminating password fatigue.
- Secure Remote Access – Enables employees, contractors, and partners to securely access corporate resources from any location.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) – Ensures users only have access to the data and applications relevant to their roles.
3. Cost Reduction
- Minimized Security Risks – IAM risk management reduces financial losses from security breaches and unauthorized access.
- Lower Compliance Costs – Automates reporting and audits, reducing penalties and administrative costs.
- Optimized Workforce Productivity – Enhances efficiency by reducing login issues and streamlining user authentication.
By integrating customer identity access management and workforce IAM, businesses can enhance security, simplify access control, and achieve significant cost savings while ensuring seamless operations.
2. Key Features of an Effective IAM Solution
Implementing a robust identity access management solution is essential for businesses looking to enhance security, streamline operations, and ensure regulatory compliance. The right IAM platform should offer key functionalities that enable secure and efficient management of user identities and access permissions. Below are the fundamental features to look for in an effective IAM solution:
1. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for Managing User Permissions
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures that users have the appropriate level of access based on their job roles.
- Reduces the risk of unauthorized access by granting permissions according to predefined policies.
- Supports the principle of least privilege, ensuring employees can only access the information necessary for their tasks.
- Enhances security and compliance by standardizing access control policies across the organization.
2. Automation of User Access Management and Reviews
- User access management automates the process of granting, modifying, and revoking access rights, reducing administrative overhead.
- Automate user access reviews ensure that only authorized users retain access to sensitive resources over time.
- Improves efficiency by integrating with HR and IT systems to update user access dynamically based on employment status and role changes.
- Reduces human errors and insider threats by eliminating manual interventions in access provisioning and de-provisioning.
3. Entitlement Management for Fine-Grained Access Control
- Entitlement management provides granular control over what users can do within applications and systems.
- Enables organizations to set permissions based on user attributes, such as department, location, or project assignment.
- Helps enforce compliance with industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) by ensuring only authorized individuals can access specific data.
- Enhances security by dynamically adjusting permissions based on real-time risk assessments.
4. Scalability to Support Growing Organizations
- Scalable IAM solutions accommodate the expanding needs of businesses by supporting an increasing number of users, applications, and devices.
- Ensures seamless integration with cloud environments, hybrid infrastructures, and multi-cloud ecosystems.
- Adapts to organizational growth by offering flexible deployment options, including on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid IAM models.
- Future-proofs security by enabling easy adoption of emerging technologies like AI-driven authentication and Zero Trust security frameworks.
Choosing the right identity access management solution is crucial for securing digital assets, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing operational efficiency. By leveraging Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), automated user access reviews, entitlement management, and scalable IAM solutions, organizations can proactively manage user identities while minimizing security risks and administrative burdens. A well-implemented IAM strategy not only strengthens cybersecurity but also optimizes business processes, improving overall productivity and cost efficiency.
3. Essential Role of IAM in Organizational Security
A well-structured IAM framework enhances security posture, strengthens compliance readiness, and streamlines identity governance and administration. Obtaining Identity Access Management certifications equips professionals with the expertise to implement and manage robust identity security strategies, benefiting both individuals and organizations.
Key IAM Certifications and Their Benefits
IAM certifications validate an individual’s proficiency in identity security, governance, and compliance. These certifications provide:
- Enhanced Security Expertise – Professionals gain in-depth knowledge of IAM risk management, authentication mechanisms, and access control best practices.
- Stronger Compliance Readiness – Certifications ensure organizations meet regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX by implementing IAM frameworks effectively.
- Career Advancement – Certified professionals stand out in the cybersecurity industry, opening doors to leadership roles in identity security.
How IAM Certifications Strengthen Security and Compliance
Organizations that invest in IAM-certified professionals benefit from:
- Improved Security Posture – Certified experts can deploy IAM solutions that prevent unauthorized access and insider threats.
- Operational Efficiency – Automating user access management and entitlement reviews reduces administrative workload.
- Regulatory Compliance – Certification ensures alignment with industry standards, simplifying audit processes and risk assessments.
Recommended IAM Certifications for IT Professionals
- Certified Identity and Access Manager (CIAM) – A comprehensive certification covering IAM best practices and governance strategies.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) – IAM Specialization – Focuses on identity governance and risk management.
- Certified Access Management Specialist (CAMS) – Ideal for professionals managing workforce IAM and customer identity access management.
- Identity Management Institute (IMI) Certifications – Includes Certified Identity Governance Expert (CIGE) and Certified Identity Protection Advisor (CIPA).
By prioritizing security training and IAM certifications, organizations can build a skilled workforce capable of mitigating security threats, managing access efficiently, and maintaining compliance in an evolving digital landscape.
4. Best Practices for Identity and Access Management (IAM)
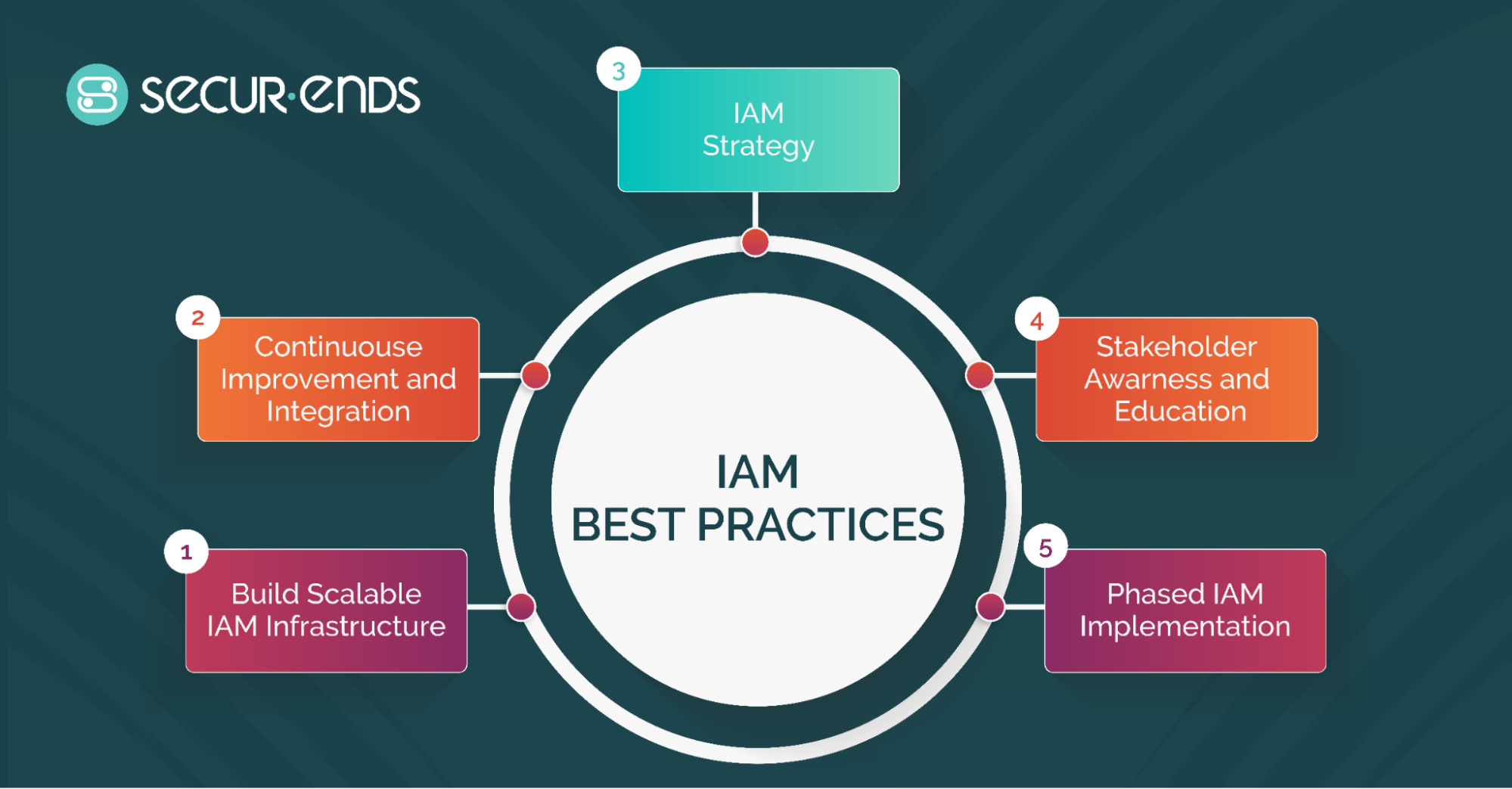
A well-implemented Identity and Access Management (IAM) strategy is essential for protecting sensitive data, reducing security risks, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. By following best practices for identity and access management, organizations can improve their security posture, streamline access management, and prevent unauthorized access. Below are key best practices that help in successful IAM implementation.
Steps to Establish a Strong IAM Framework
An effective IAM framework must be strategic, proactive, and continuously evolving to keep pace with security threats and organizational changes. Here are key steps to build a strong IAM foundation:
- Define IAM Policies and Access Controls:
-
-
- Develop a clear IAM policy outlining user roles, authentication mechanisms, and access permissions based on the principle of least privilege (PoLP)—granting users only the minimum level of access needed for their tasks.
- Establish strict privileged access management (PAM) for users with administrative or sensitive data access.
-
- Adopt Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
-
-
- Implement MFA across all systems to add an extra layer of security, ensuring users verify their identity through multiple authentication factors (e.g., passwords, biometrics, or security tokens).
- Enforce adaptive authentication techniques that analyze user behavior, location, and device health before granting access.
-
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC):
-
-
- RBAC assigns predefined access based on a user’s role within the organization, simplifying permission management.
- ABAC enhances security by granting access dynamically based on user attributes, location, or device type, allowing greater flexibility.
-
- Enforce Just-In-Time (JIT) Access:
-
-
- Instead of granting long-term privileged access, JIT access provisions temporary, time-limited permissions for specific tasks, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
- Particularly useful for contractors, third-party vendors, and short-term projects.
-
- Leverage Passwordless Authentication Methods:
-
-
- Reduce password-related security risks by implementing biometric authentication, hardware tokens, or single sign-on (SSO) solutions.
- Passwordless authentication minimizes the risks of phishing attacks and brute force login attempts.
-
- Automate IAM Workflows:
-
- Automate user onboarding, access provisioning, and deprovisioning to reduce human errors and enhance operational efficiency.
- Automated IAM solutions ensure that employees, vendors, and partners receive appropriate access immediately upon joining and have access revoked upon exit.
5. Regular User Access Reviews to Prevent Entitlement Creep
Entitlement creep occurs when users gradually accumulate excessive or outdated access permissions, increasing security risks. To mitigate this, organizations should:
- Conduct periodic user access reviews to validate whether users still require their assigned permissions.
- Audit orphaned accounts—inactive or ex-employee accounts that retain system access—to prevent unauthorized use or exploitation by attackers.
- Monitor privileged accounts to ensure that administrative users have only the necessary level of access and are not misusing their permissions.
- Centralize log collection and analysis to maintain a clear history of user activity, helping security teams identify unusual access patterns or insider threats.
Proactive access reviews reduce security risks by ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to critical systems and sensitive data.
Integration of IAM with Existing Security Tools
For a comprehensive IAM strategy, organizations must ensure that IAM solutions work in harmony with other security tools to create a seamless, defense-in-depth approach:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):
-
-
- Integrating IAM with SIEM tools helps detect unauthorized access attempts, insider threats, and login anomalies in real time.
- Correlating IAM logs with security incidents improves threat detection and response.
-
- Endpoint Security Solutions:
-
-
- Extend IAM policies to laptops, mobile devices, and other endpoints to prevent unauthorized access through compromised devices.
- Deploy endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions to identify and block threats targeting user credentials.
-
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs):
-
-
- As organizations adopt cloud services, IAM should integrate with CASBs to monitor user access, detect suspicious behavior, and enforce security policies across cloud applications.
- Protects against data leaks, misconfigured cloud storage, and unauthorized data sharing.
-
- Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR):
-
- AI-driven ITDR solutions analyze user behavior to detect anomalies and automatically respond to identity-related threats.
- Helps prevent account takeovers, compromised credentials, and insider attacks.
By integrating IAM with these security solutions, businesses can strengthen security defenses, improve compliance, and reduce the risk of identity-related threats.
6. Identity Access Management (IAM) Tools and Methods
Effective Identity and Access Management (IAM) relies on robust tools and methodologies to secure user access and prevent unauthorized entry into critical systems. Organizations use various IAM solutions to authenticate, authorize, and manage identities efficiently. Below is an overview of the most widely used IAM tools, authentication methods, and the differences between on-premises and cloud-based IAM solutions.
Popular Identity and Access Management Tools
Several IAM tools are available to help organizations strengthen their security posture and streamline access management. Some of the most widely adopted solutions include:
- Okta – A cloud-based IAM solution that provides Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and adaptive access controls to enhance security while ensuring seamless user experiences.
- Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) – Microsoft’s IAM platform that offers identity protection, role-based access control (RBAC), and integration with Microsoft 365 applications.
- SecurEnds – A tool that focuses on identity governance and administration (IGA), automating access reviews and identity lifecycle management to ensure compliance and security.
- Ping Identity – A solution that delivers advanced authentication, identity federation, and API security to protect enterprise environments.
- IBM Security Verify – An IAM platform that offers AI-powered security insights, adaptive authentication, and access governance for hybrid cloud environments.
IAM Methods and Authentication Techniques
Organizations implement various IAM authentication methods to enhance security and ensure only authorized users gain access to sensitive data. Some of the most effective IAM methods include:
- Single Sign-On (SSO) – Allows users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications without needing to enter credentials repeatedly. This enhances convenience while reducing password-related security risks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Strengthens authentication by requiring users to provide multiple verification factors, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time passcodes, before accessing resources.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) – Assigns permissions based on predefined roles within the organization, ensuring users only have access to resources necessary for their job functions.
- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) – Uses dynamic policies based on user attributes, such as department, location, or job function, to determine access rights.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM) – Focuses on securing high-privilege accounts by implementing strict access controls and session monitoring.
To ensure effective identity management, organizations must also decide how to deploy their IAM solutions. The choice between on-premises and cloud-based IAM systems depends on factors such as security control, scalability, and integration capabilities.
On-Premises vs. Cloud-Based IAM Solutions
Organizations can choose between on-premises and cloud-based IAM solutions based on their security requirements and infrastructure. Each has distinct advantages and challenges:
- Deployment – On-premises IAM solutions are hosted within an organization’s internal network, offering full control over security configurations. IAM in cloud computing solutions are hosted on external cloud platforms, providing flexibility and scalability.
- Security Control – On-premises IAM gives organizations complete control over their security framework, making it ideal for industries with strict compliance mandates. Cloud-based IAM shifts security responsibilities to the service provider while ensuring ongoing updates and threat protection.
- Scalability – Expanding an on-premises IAM system requires additional hardware and resources, whereas cloud-based IAM solutions can scale easily to accommodate growing business needs.
- Cost – On-premises IAM entails high upfront costs for hardware, software, and IT management, while cloud-based IAM follows a subscription model, reducing capital expenditure and providing cost predictability.
- Integration – On-premises IAM may require complex configurations to integrate with cloud applications, while cloud-based IAM solutions seamlessly integrate with SaaS applications and other cloud-native security tools.
IAM tools and authentication methods play a critical role in modern security strategies. Organizations must choose the right IAM solutions based on their security needs, compliance requirements, and infrastructure capabilities. Whether opting for on-premises or cloud-based IAM, implementing best practices such as SSO, MFA, and RBAC ensures a secure and efficient identity management framework.
7. Implementing Identity Access Management (IAM)
In an era where digital security is paramount, Identity Access Management (IAM) plays a critical role in securing access to Content Management Systems (CMS). By implementing IAM solutions, organizations can control user permissions, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure secure content management.
Importance of Securing CMS with IAM Solutions
IAM solutions help enforce security policies by enabling role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and audit logging. These features reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized modifications to digital assets.
Integration of IAM with Popular CMS Tools
Most leading CMS platforms, such as WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla, support IAM integration through plugins, extensions, or API-based connections. By integrating IAM, businesses can streamline user authentication and enhance security across their content ecosystem.
Examples of IAM Enhancing Content Security and Management
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple authentication steps.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Simplifies login processes by allowing users to secure content access in multiple systems with a single set of credentials.
- Granular Access Controls: Ensures that only authorized users can edit, publish, or delete content, reducing the risk of accidental or malicious changes.
By implementing IAM, businesses can protect sensitive content, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
8. IAM Tools: Selecting the Best Solutions
As cyber threats evolve, Identity and Access Management tools have become a fundamental component of modern security frameworks. Organizations must carefully choose the right IAM software to ensure secure access, prevent data breaches, and comply with regulatory requirements. A well-implemented IAM framework not only enhances security but also streamlines identity verification, making it easier to manage user roles and permissions across digital ecosystems.
Key Features to Look for in Identity and Access Management Tools
Selecting the right IAM solution requires a deep understanding of security needs and organizational requirements. Below are the key features businesses should consider:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigns access privileges based on user roles, reducing the risk of unauthorized data exposure.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra security layer by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Allows users to log in once and gain access to multiple applications, improving security and user experience.
- Identity Federation: Integrates IAM tools with external identity providers (such as Google or Microsoft Entra ID) to facilitate seamless authentication.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Protects high-level accounts from unauthorized access and insider threats.
- User Lifecycle Management: Automates onboarding and offboarding processes, ensuring that access permissions are updated as employees change roles or leave the organization.
- Risk-Based Authentication (RBA): Uses AI and behavioral analytics to assess login risks dynamically and apply additional security measures when needed.
- Audit Logging & Compliance Reporting: Keeps track of user activities to detect security incidents and ensure compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 regulations.
Comparison of Leading IAM Tools and Their Capabilities
Several IAM solutions stand out in the market, each offering unique security and identity management capabilities.
- Okta – A cloud-based IAM tool known for its strong SSO and MFA features. It provides seamless integration with various applications, making it an ideal choice for businesses that require scalability and ease of use.
- Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) – Designed for enterprises using Microsoft services, this solution offers identity federation, conditional access policies, and deep integration with Microsoft 365 and Azure environments. It is a preferred option for businesses looking to secure their Microsoft-based infrastructure.
- Ping Identity – A robust IAM solution that includes AI-powered threat detection, API security, and strong identity governance. It is commonly used by large enterprises that require high levels of authentication security and flexibility in integration.
- IBM Security Verify – This tool provides advanced identity governance, AI-driven IAM risk management, and adaptive authentication. It is suitable for organizations needing a highly customizable IAM framework with a focus on compliance and risk reduction.
- CyberArk – Primarily focused on Privileged Access Management (PAM), CyberArk helps organizations protect high-risk accounts and prevent insider threats. It is widely adopted in industries that handle sensitive data, such as finance and healthcare.
SecurEnds – A rising player in IAM, SecurEnds specializes in identity governance, user access certification, and role management automation. It is particularly beneficial for businesses seeking an easy-to-deploy solution with AI-powered analytics for enhanced security compliance.
Benefits of Using Top IAM Solutions

Investing in the right IAM framework delivers significant benefits beyond just security:
- Enhanced Protection Against Cyber Threats – IAM tools prevent unauthorized access, reducing the risk of data breaches, identity theft, and insider threats.
- Regulatory Compliance – Many industries require organizations to follow strict security protocols (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2). IAM tools help businesses stay compliant with audit trails and real-time monitoring.
- Improved User Experience – Features like SSO and adaptive authentication simplify the login process while maintaining security. Users can seamlessly access multiple applications without multiple logins.
- Operational Efficiency – Automating identity provisioning and deprovisioning reduces IT workload and ensures that employees have the right access at the right time.
- Risk Management and AI-Driven Insights – Some IAM solutions, such as SecurEnds and Ping Identity, leverage artificial intelligence to detect suspicious activities and dynamically adjust access permissions based on risk assessment.
By carefully evaluating business needs and comparing available solutions, organizations can implement an IAM software that enhances both security and productivity.
9. IAM and RBAC: A Perfect Match
As organizations expand their digital operations, securing sensitive information while ensuring seamless access for authorized users becomes crucial. Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) work together to provide a structured, secure, and scalable solution for managing user access. By integrating RBAC within IAM frameworks, businesses can enforce least privilege principles, reduce security risks, and streamline compliance with regulatory standards.
Definition and Working of RBAC in the IAM Context
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a security model that restricts system access based on predefined roles within an organization. Instead of assigning permissions to individual users, RBAC groups users based on their job functions and grants them specific access rights accordingly.
In the IAM ecosystem, RBAC works by:
- Defining roles based on job responsibilities (e.g., HR Manager, IT Administrator, Finance Executive).
- Assigning permissions to these roles rather than individual users.
- Automatically granting or revoking access when users change roles, departments, or leave the organization.
By implementing IAM with RBAC, companies can reduce manual access management efforts while ensuring strict control over sensitive data and critical applications.
Benefits of Implementing RBAC for Security and Compliance
RBAC, when integrated into an IAM framework, provides multiple advantages:
- Enhanced Security – Ensures that users only have access to the information necessary for their job, reducing risks related to insider threats and privilege escalation attacks.
- Regulatory Compliance – Helps businesses adhere to data protection laws (GDPR, HIPAA, SOX) by enforcing strict entitlement management and access audit trails.
- Operational Efficiency – Automates access assignments, reducing IT workload and eliminating manual access approval bottlenecks.
- Scalability and Flexibility – Supports IAM risk management by allowing organizations to scale access controls as business needs evolve.
- Minimized Human Error – Prevents accidental over-provisioning of permissions, reducing security vulnerabilities.
Case Studies of RBAC in Action Across Industries
- Healthcare Industry – A hospital implemented RBAC within its IAM system to control access to patient records. Doctors had read-only access to medical histories, while administrators could edit patient data. This structure ensured HIPAA compliance while maintaining efficient workflows.
- Financial Services – A multinational bank used IAM with RBAC to restrict access to sensitive financial transactions. Lower-level employees had limited access, while senior analysts had broader permissions. This helped prevent fraud and ensure adherence to SOX regulations.
- Retail and E-Commerce – A global e-commerce company deployed RBAC-driven scalable IAM solutions to manage seasonal employees and contractors. Temporary workers received restricted access, while full-time employees had broader permissions, reducing security risks during high-traffic sales periods.
By combining IAM and RBAC, businesses can create a scalable IAM solution that enhances security, compliance, and operational efficiency. Whether in healthcare, finance, or retail, RBAC ensures that access control remains structured, automated, and risk-free.
10. Integrating IAM with Existing IT Ecosystems
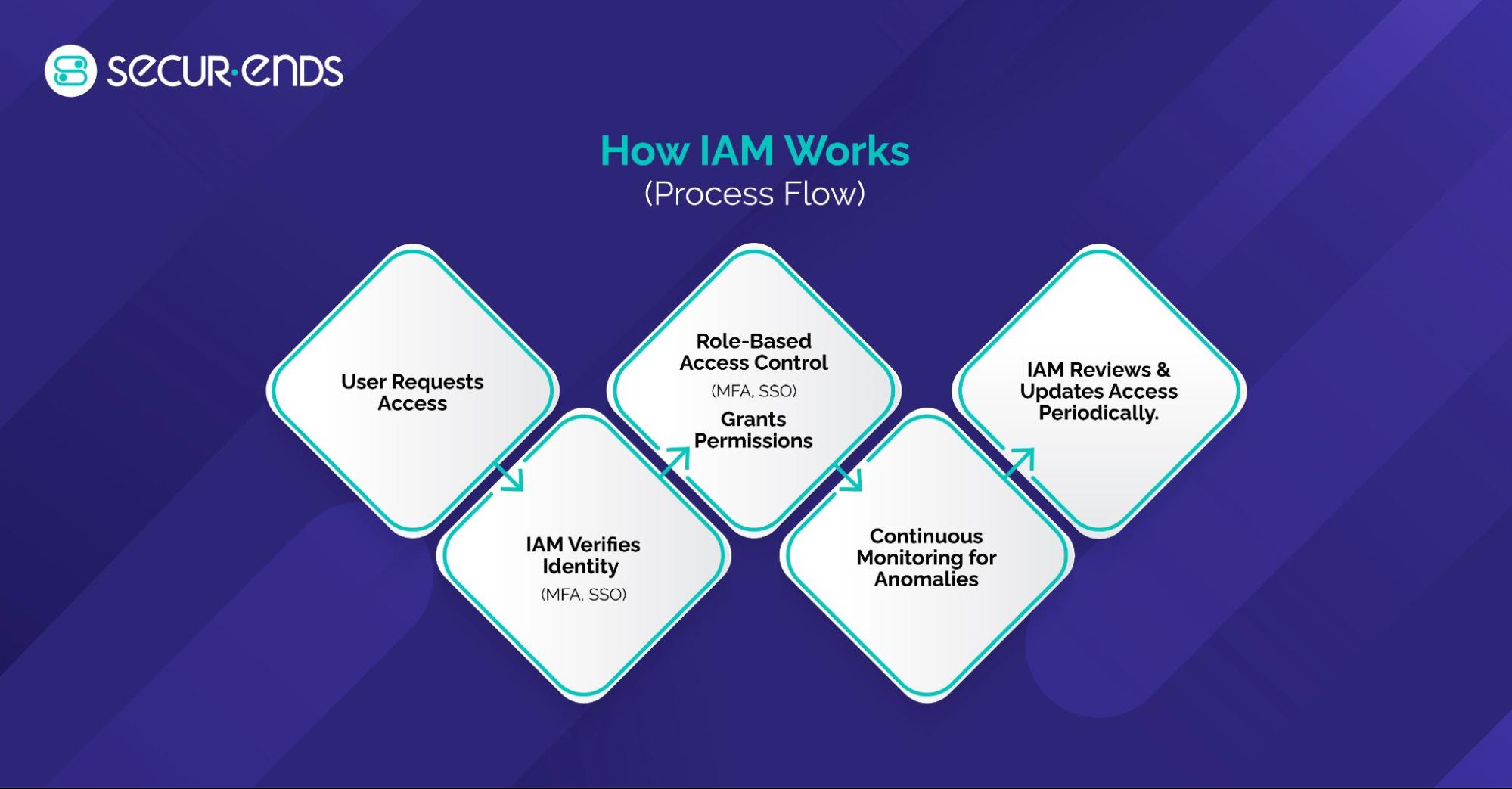
As businesses grow, integrating Identity and Access Management (IAM) with existing IT systems is crucial for data security and operational efficiency. Connecting IAM solutions to tools like Okta, Workday, and other enterprise platforms helps streamline user access, ensure regulatory compliance, and protect data.
- Okta Integration: Okta provides single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), allowing secure access to multiple systems. Integrating it ensures consistent identity management and reduces administrative work.
- Workday Integration: Workday manages HR and payroll, and IAM integration ensures that employee data and access are securely controlled, automating user provisioning and role-based access to sensitive data.
Other Systems: IAM can also integrate with CRM systems, cloud storage, and ERP tools, ensuring secure and consistent identity management across all platforms.
11. Steps for Seamless Integration:
- Assess Compatibility: Check if y/our IAM solution supports integration with your existing systems.
- Map Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and ensure IAM policy reflects them for smooth provisioning.
- Implement SSO: Allow users to log in once and access multiple systems.
- Test and Validate: Run test integrations to ensure IAM works across all systems.
- Monitor and Maintain: Regularly review access and adjust IAM policies as needed.
IAM Benefits of Integration:
- Scalability: IAM helps manage growing user bases by automating role-based access updates.
- Efficiency: Automating identity processes (e.g., user provisioning, password management) reduces administrative tasks, letting IT teams focus on strategic work.
Integrating customer Identity Access Management into your IT ecosystem creates a secure, efficient, and compliant environment that supports business growth and protects data.
12. The Business Benefits of IAM
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is not just about securing data—it also helps improve business operations by ensuring data security, supporting regulatory compliance, and boosting operational efficiency. When used effectively, IAM can streamline processes and protect organizations from risks like data breaches or insider threats.
Improving Compliance and Reducing Regulatory Risks
One of the biggest advantages of IAM is how it helps organizations comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. These rules require strict control over who has access to sensitive data. IAM supports compliance by:
- Enforcing strict access controls: Ensures only authorized people have access to sensitive data.
- Providing audit trails: Tracks user activities, making it easier to demonstrate compliance during audits.
- Automating compliance checks: Regularly checks and updates access permissions to meet legal requirements.
By automating compliance and enforcing strong access controls, customer Identity Access Management reduces the risk of fines and penalties.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency through Automation
IAM improves operational efficiency by automating tasks like user account creation, access management, and password resets. This saves time and reduces the risk of human error. Key ways IAM boosts efficiency include:
- Automated user provisioning: Automatically grants or revokes access when employees join or leave.
- Self-service options: Users can reset their own passwords, freeing up IT resources.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Automatically gives users access based on their job roles, ensuring consistency and reducing errors.
These efficiencies allow IT teams to focus on more strategic tasks and reduce the burden of manual access management.
Reducing Risks of Insider Threats and Data Breaches
Additional IAM benefits are, it helps reduce the risk of insider threats and data breaches by ensuring that access to sensitive information is tightly controlled. IAM reduces these risks through:
- Granular access controls: Implementing IAM policy, restricts access to only those who need it, based on their role.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Adds extra layers of security beyond just passwords.
- Behavioral analytics: Identifies unusual user activities that might indicate a security breach.
- Privileged access management: Monitors high-level accounts to prevent misuse.
Together, these features help safeguard sensitive data, reducing the chances of breaches or insider attacks.
By streamlining data security and automating processes, IAM enables organizations to focus on growth and innovation while maintaining security and compliance.
13. IAM Trends for 2025
As Identity and Access Management (IAM) continues to evolve, several key trends will shape the future of digital security in 2025. The integration of AI, machine learning, and cloud environments will redefine how businesses manage access, protect data, and maintain compliance. Below are the most impactful modern IAM trends that organizations must embrace to stay secure and competitive:
The Rise of AI-Driven Identity Management
In 2025, AI in identity management will revolutionize how organizations manage user access and secure digital environments. Artificial intelligence (AI) will enable IAM systems to be more adaptive, intelligent, and proactive in detecting security threats. Key developments include:
- Automated threat detection: AI systems will leverage machine learning to identify anomalous user behavior, flagging potential breaches before they escalate.
- Real-time authentication adjustments: AI will analyze contextual factors such as location, device, and user behavior to dynamically adjust authentication requirements, ensuring access is granted securely based on real-time risk assessments.
- Enhanced access decision-making: AI will improve the decision-making process, automating access control to ensure policies are enforced consistently, reducing the need for manual oversight.
The integration of AI will make IAM systems more efficient and intelligent, reducing the risk of insider threats and improving overall security management.
Expanding IAM Capabilities for Cloud and SaaS Applications
As businesses continue their digital transformation, there will be an increased demand for IAM solutions that can support cloud and SaaS (Software as a Service) platforms. By 2025, IAM systems will offer enhanced capabilities to manage access in these cloud-driven environments. Key trends include:
- Cloud IAM: IAM systems will increasingly be optimized for cloud platforms like AWS and Azure, ensuring secure and seamless management of user identities and access across both on-premise and cloud applications.
- Improved integrations with SaaS: As businesses deploy more SaaS applications, IAM will ensure that security is maintained across these tools, offering Single Sign-On (SSO) and federated identity management to streamline access across multiple cloud services.
- Identity governance in the cloud: With the rise of cloud services, IAM will integrate better with cloud-native security tools to help organizations enforce consistent security policies and maintain compliance across both cloud and on-premise environments.
As cloud and SaaS applications continue to dominate, IAM solutions will evolve to handle the growing need for secure access management across multi-cloud infrastructures.
Predictions for Hybrid IT Environments and IAM Developments
With the increasing adoption of hybrid IT environments—where organizations utilize a mix of on-premise systems and cloud infrastructure—IAM systems will need to provide greater flexibility and scalability. In 2025, we can expect the following:
- Unified IAM solutions: As hybrid IT environments become the norm, IAM solutions will offer centralized management, allowing businesses to secure and govern access across on-premise data centers and cloud environments.
- Role-based and attribute-based access control (RBAC & ABAC): IAM systems will evolve to provide more sophisticated access management, supporting both RBAC and ABAC to address the complex needs of hybrid infrastructures.
- Hybrid cloud IAM frameworks: New IAM in cloud computing solutions will be designed with hybrid cloud architectures in mind, ensuring organizations can maintain security, compliance, and efficiency across diverse IT ecosystems.
Hybrid environments will require scalable and unified IAM systems capable of managing complex access needs across both traditional and modern infrastructures.
The IAM landscape in 2025 will be shaped by the rise of AI-driven identity management, the evolution of IAM for cloud and SaaS applications, and the continued growth of hybrid IT environments. As IAM becomes increasingly critical for organizational security, businesses will need to adapt to these trends to ensure that access is managed securely, efficiently, and in line with emerging technologies.
14. Difference Between IAM and IGA
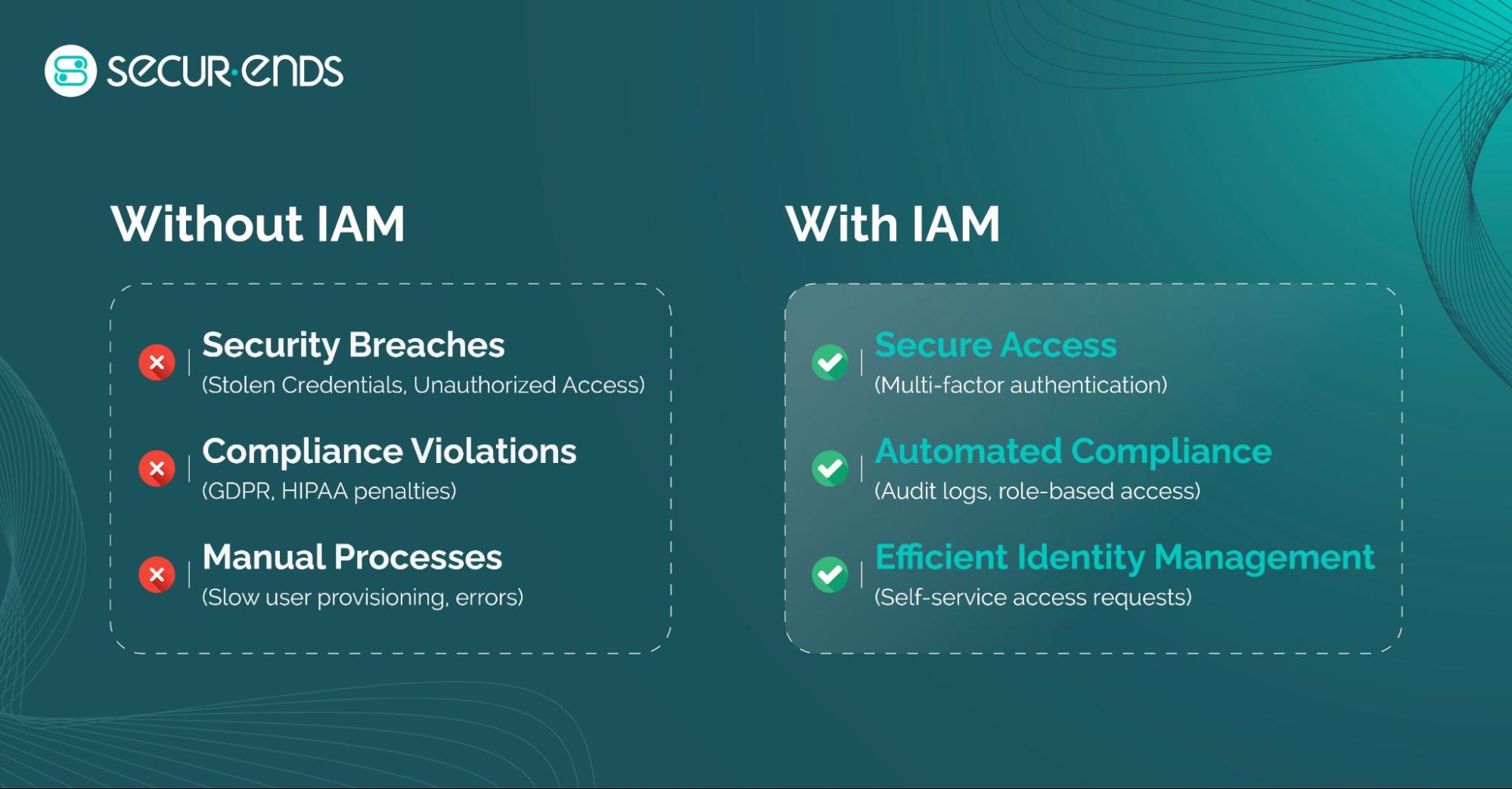
Understanding the distinction between Identity Governance vs Identity Management is crucial for creating an effective identity strategy. While both are crucial for security, they address different aspects of identity management. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
What is IAM and IGA?
- IAM (Identity and Access Management) focuses on managing digital identities, controlling user access to resources and IAM risk management. It ensures users can securely access the right systems and data at the right time. Key elements include:
- Authentication: Verifying user identity (e.g., through passwords or multi-factor authentication).
- Authorization: Defining user permissions.
- Access Control: Managing how users interact with resources.
- IGA (Identity Governance and Administration) has a broader focus, emphasizing governance, compliance, and ensuring access is properly managed according to policies and regulations. It includes:
- Governance: Setting and enforcing access policies.
- Provisioning/Deprovisioning: Managing user account lifecycles.
- Access Reviews: Ensuring regular audits to meet compliance standards.
Understanding the difference between governance vs access management is essential for organizations aiming to build a robust and secure identity management strategy.
IAM vs IGA: Key Differences
- IAM focuses on real-time access control, ensuring users are authenticated and authorized to access resources.
- IGA focuses on governance, ensuring policies are followed, access rights are reviewed, and compliance is maintained.
How They Work Together
- IAM supports IGA solutions by enabling secure user access.
IGA supports IAM by reviewing access rights and ensuring they comply with organizational policies, regulations and IGA security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Identity and Access Management (IAM) is an essential framework for modern organizations, safeguarding both digital identities and sensitive data. From securing user access to ensuring compliance with industry regulations, IAM solutions play a pivotal role in reducing risks and enhancing operational efficiency. By adopting the right IAM tools, policies, and best practices, organizations can improve security posture, streamline operations, and stay ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. As we move toward a more integrated and cloud-based future, embracing IAM will be key to maintaining security, scalability, and efficiency across business ecosystems.